How fingerprints are used for identification
Finger biometrics use ridgeline patterns and details on the surface of fingerprints to uniquely identify a person. This type of biometric authentication is widely used in large-scale government and law enforcement applications due to their accuracy. The availability of robust commercial solutions like Ziphio platform has helped popularize fingerprint recognition for smartphones and other personal devices.
Fingerprint biometric image – Fingerprint Recognition – Biometric Authentication, DaonHow fingerprints are used for identification
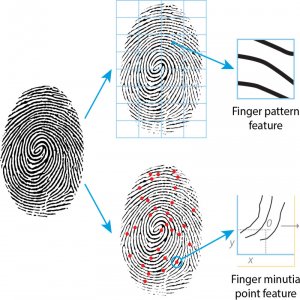
Pattern-based finger algorithms subdivide the fingerprint image into smaller cells and compare the ridgeline patterns in each cell. This technique works well with the small silicon finger sensors found on smartphones
Where a higher quality, larger optical sensor is used, such as for border control or national identity projects, additional details relating to the ridgelines are used. The location coordinates of where the finger ridge lines end or split into two lines, called minutiae points, provide additional unique information. A single flat fingerprint image can contain up to 30 unique minutiae points.
One fingerprint provides sufficient information to accurately verify a person, but four to 10 fingers are recommended to uniquely identify a person within a large population database
Applications of fingerprint recognition
Finger capture is fast; most finger solutions simply require the finger to be placed on a flat sensor. Contactless capture solutions are also beginning to emerge, where a video of the fingers is taken at a distance.
Fingerprint accuracy varies across solutions and smartphones as different algorithms and sensors are used. Performance is better with larger sensors, guided positioning, and good user feedback and familiarity.
The fingerprint function on mobile devices ensures that fingerprint data is enrolled by the phone’s operating system, stored in a secure component on the device and can only be used on that device. This may mean that other biometric options may be preferable for situations where a user needs to be authenticated across different devices or where the enrollment process needs to more controlled.
Suitability of fingerprint recognition
-
- Permanence: Fingerprints do not change with ageing. As you get older, fingerprints can get harder to read. IdentityX can enroll multiple fingers reducing the likelihood of an authorized individual being denied access.
-
- Flexibility: IdentityX allows you to enroll multiple fingers which avoids potential issues of not granting access after an injury.
-
- Quality: False Acceptance Rate (FAR) is highly dependent on the quality of your fingerprint reader.
-
- Collectability: Fingerprints are easy to acquire. Avoid using fingerprint readers without liveness detection.